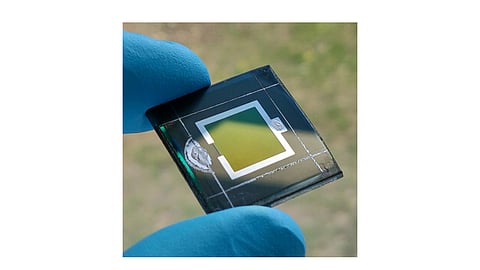

Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) of Germany has announced achieving power conversion efficiency level of 24.16% for a tandem cell comprising perovskite and CIGS technologies. The efficiency has been certified by the CalLab of the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE).
To achieve this level, HZB used a trick the team developed earlier – this is first placing SAM molecules on the CIGS layer that are 'self-organized in close proximity to a monomolecular layer'. The perovskite layer was deposited in the HySPRINT lab at the HZB directly on the rough CIGS layer.
"This time we connected the lower cell from CIGS directly to the upper cell from perovskite, so that the tandem cell only has two electrical contacts, so-called 'terminals'," explains Dr. Christian Kaufmann from PVcomB at HZB, who developed the CIGS sub-cell with his team. "The introduction of rubidium in particular has significantly improved the CIGS absorber material." According to the team, this combination can be a good fit for satellite technology in space applications.
Results of this research have been published in the international journal Joule.
In February 2019, HZB reported 21.6% power conversion efficiency for pure perovskite & CIGS thin-film tandem solar cells while sharing plans of offering independent advisory services for BIPV technology.
.png?w=50&fm=png)