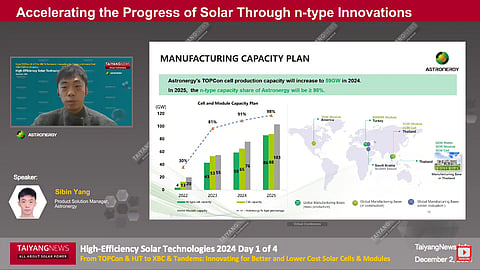

Astronergy is expected to reach up to 59 GW of TOPCon cell production capacity by the end of 2024, aligning with the global trend of cell technology adoption
The latest TOPCon 4.0 series cell structure features several technological advancements such as laser-induced firing, metallization paste optimization, and POML technology
The company's latest ASTRO N8 series bifacial module, equipped with 66 210 x 210 mm TOPCon 4.0 series cells, double 2 mm-glazed high-transparency glass, and LRF film, can deliver up to 720 W of power output
Astronergy also introduced its special offshore PV design tailored for floating PV applications, which can be incorporated into ASTRO N7, N8, and N5 series modules
The evolving trends in TOPCon PV module applications – spanning utility-scale with or without trackers, distributed systems, and offshore applications – are primarily driven by market dynamics. Continuous improvements in cell efficiency, module design optimization, and innovations in the bill of materials (BOM) are key to making TOPCon products globally competitive.
Sibin Yang, Product Solution Manager at Astronergy, provided a brief overview of global market demand for TOPCon cell technology and the latest advancements in application-specific TOPCon modules at the recent TaiyangNews High Efficiency Solar Technologies 2024 Conference (see Astronergy presentation here). Founded in 2006, the Chinese PV cell and module manufacturer transitioned from PERC to TOPCon technology in 2022 and launched its upgraded ASTRO N7 series of n-type TOPCon PV modules in 2023.
Yang opened his presentation with a competitive analysis of leading cell technologies: TOPCon, HJT, XBC, and Perovskite Tandem. He pointed out that while each technology has its pros and cons, TOPCon-based modules have emerged as the primary choice for several tier-1 PV module manufacturers, largely due to their lower production costs. According to InfoLink Consulting's August 2024 data, the total production cost of a traditional HJT module is 15.9 RMB/W higher than that of TOPCon, while HJT modules with 0BB and silver-coated copper metallization paste are 4.5 RMB/W more expensive. However, the production cost for the back-contact (BC) cell structure based on TOPCon, or TBC, is 10.2 RMB/W higher compared to TOPCon. This reveals further scope for improvement in HJT and XBC technologies to match TOPCon’s mass-scale production costs. As a result, multiple tier-1 vertically integrated PV module manufacturers have rapidly adopted the TOPCon cell structure.
By the end of 2028, TOPCon capacity is expected to reach up to 2,065 GW, while capacities for HJT and XBC are projected to reach 469 GW and 164 GW, respectively, according to the InfoLink Consulting's August 2024 report. In line with this market trend, Astronergy’s TOPCon cell production capacity will increase to 59 GW by the end of 2024, bringing its share of n-type capacity to over 98% by 2025.
The latest ASTRO N – TOPCon 4.0 series cell technology, the core component of the TOPCon module, includes several technological advancements such as laser-induced firing, metallization paste optimization, and POML technology – an upgraded rear poly-Si passivation technology. Laser-induced firing reduces damage to the passivation layer during metal-silicon contact formation, enhancing cell efficiency. Metallization paste optimization improves product reliability, while the advanced rear-side passivation technology, using multi-layer doped poly-Si (POML), reduces parasitic absorption, boosts Voc and lsc, and ultimately increases cell efficiency.
In addition to the upgraded cell technology, Astronergy has incorporated light-redirecting film (LRF) and high-transmittance double-layer PV glass into the design of its TOPCon PV modules. The LRF, featuring a 120° reflective microstructure surface, provides full reflection of incident light (as opposed to diffuse reflection in conventional coatings), boosting front-side power by up to 2 W. The double-layer PV glass, with 94.2% transparency and consisting of an upper layer of closed-cell film and a lower layer of SiO2 structure, delivers a power gain of 1 W – 2 W and improves moisture resistance compared to conventional coated PV glass with 93.9% transparency.
By integrating these advancements, Astronergy is promoting 2 models for utility-scale applications: the ASTRO N7 and ASTRO N8 series, and the ASTRO N7s black module for distributed markets. The company has shifted its wafer sizes from M10 and M10R to G12 and M12R for utility-scale modules, aligning with global market trends. The ASTRO N7 series, launched in 2023, features 66 210R-size TOPCon 4.0 series 16BB cells, double 2 mm-glazed high-transparency glass, and LRF film, offering a power output of up to 630 W. With dimensions of 2,382 x 1,134 x 30 mm, this module is suitable for utility applications with tracker systems.
The newest ASTRO N8 bifacial series, equipped with 66 210 x 210 mm TOPCon 4.0 series cells, double 2mm-glazed high-transparency glass, and LRF film, can deliver up to 720 W of power output. A tracker with 4 strings (4x28) of ASTRO N7 615 W modules can achieve a 12.3% higher power output compared to a tracker with 4 strings (426) of ASTRO N5 590 W modules. Meanwhile, a tracker with 3 strings (3x28) of ASTRO N8 710 W modules can generate 2.8% less power. For 2P fixed-tilt rack installations, the ASTRO N8 modules can deliver up to 29.6% higher rack power compared to ASTRO N5 modules.
Astronergy also introduced its special offshore PV design, featuring high-edge sealing, insulation, corrosion resistance, and high mechanical strength, tailored for floating PV applications. This design can be incorporated into ASTRO N7, N8, and N5 series modules. Additionally, the new ASTRO N7 module series, featuring 2,000 V system voltage and dimensions of 2,390 x 1,142 x 30 mm, can reduce the balance of system (BOS) costs by up to 0.29 c$/W and enhance power yield by up to 1% for 38 pieces of series connected modules in a string.
