
DMEGC presented results from extended bankability and third-party reliability testing across its advanced module platforms
The company integrates reliability at the architecture level through double-glass designs, lightweight formats, and region-specific module adaptations
Reinforced glass and high-load module configurations were presented to address growing exposure to hail and extreme weather conditions
As module formats increase in size and power output, reliability is increasingly linked to structural design, material selection, and extended stress validation. Beyond standard IEC qualification, manufacturers are increasingly expected to demonstrate resilience under combined environmental stresses, such as UV exposure, humidity, hail impact, and mechanical loading.
At the TaiyangNews Reliable PV Module Conference, DMEGC Solar presented its reliability strategy for next-generation module platforms. The presentation, titled "Integrating Reliability into Advanced PV Module Architectures", emphasized long-term performance rather than efficiency metrics alone.
Speaking at the event, Alejandro Coll García, Product Manager Southern Europe at DMEGC Solar, explained that reliability must be addressed holistically. Founded in 1980 and entering photovoltaics in 2009, DMEGC now operates in both cell and module production. The company said reliability should not be limited to cell architecture but should be addressed across certification, materials, manufacturing processes, and module design.
Coll García also highlighted the importance of long-term stability beyond product performance. PV projects typically operate for 20 to 25 years, making financial resilience and controlled capacity expansion equally important.
DMEGC reports using 100% green electricity in both cell and module manufacturing and operating a zero-carbon factory. The company states that the carbon footprint of its modules is below 450 kg CO₂. It has also received EcoVadis Silver recognition and reports PFAS-free module production alongside compliance with French Eco-Passport requirements.
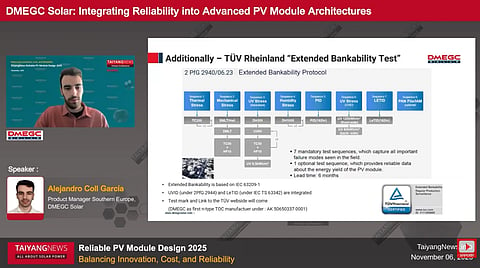
A major point of discussion during the presentation was on extended reliability validation beyond standard IEC testing. DMEGC claims to be the first PV manufacturer in China to complete TÜV Rheinland’s Extended Bankability Protocol under IEC TS 63209. The company also received TÜV Rheinland’s All Quality Matters (AQM) reliability recognition under the 2PfG 2944 testing protocol.
The extended bankability validation was conducted on DMEGC’s G12 RTB66 utility module platform, with degradation remaining below the 5% threshold defined under the protocol.
Under TÜV Rheinland’s AQM (2 PfG 2944) testing, UV-induced degradation (UVID) remained below 0.7% following 120 kWh/m² front and 60 kWh/m² rear exposure, staying within the 1.5% requirement defined under updated specifications, says Coll García.
DMEGC established an in-house laboratory in 2023, which was inspected by TÜV Rheinland. The facility is used for application-specific testing, compatibility assessments with mounting structures and trackers, and internal quality monitoring.
Beyond certification and laboratory validation, the presentation emphasized module architecture as a key lever for reliability. Coll García noted that earlier monofacial TOPCon designs faced humidity-related exposure challenges. To address this, DMEGC introduced double-glass configurations that enhance environmental protection while delivering approximately 1% performance gain. Full-black residential modules in this configuration reach 460-465 W.
For space-constrained rooftops, DMEGC presented a compact ‘installer-friendly’ module platform. The M10T-B32HBT module measures 1,542 × 766 × 30 mm and weighs 15.3 kg, making it smaller and lighter than conventional residential formats. The design supports mechanical loads up to 8,100 Pa, a 50% increase in maximum pressure load. In comparative rooftop layouts shown during the presentation, total system capacity increased from 5.4 kWp to 6.9 kWp on the same roof area.
For load-sensitive rooftops, particularly in the French market, the company introduced a lightweight module (DMxxxM10RT-54HSW-L). The module weighs 15 kg (7.5 kg/m²) and is designed for buildings where structural limits restrict standard installations. The configuration supports mechanical loads of +3,600 Pa to -2,400 Pa and achieves a power rating of 460-465 W using 1.6 mm single-glass construction.
For overhead installations, especially in Germany, modules must qualify as construction materials. DMEGC holds DIBt certification for this segment, using specific bill-of-material configurations to meet structural safety requirements.
Hail resistance was another focus area. The company presented reinforced glass configurations with 3.2 mm front glass and 2.0 mm rear glass, enabling resistance to 40 mm hail at 100 km/h. Mechanical load ratings reach 8,100 Pa on the front and 3,600 Pa on the rear. An extreme configuration with 4.0 mm glass withstands 50 mm hail at 110 km/h. According to Coll García, demand for reinforced modules is increasing in regions exposed to severe weather events.
The company’s portfolio also includes greenhouse-compatible modules for agrivoltaic integration, anti-glare modules for airport-adjacent installations, and application-specific variants targeting European regulatory requirements.
The full presentation is available on the TaiyangNews YouTube channel here.
