
Compared to standard solar cell processing, HJT requires a completely different manufacturing setup. However, the wet-chemical process is somewhat an exception, as the basic process steps remain the same – saw damage removal, texturing and cleaning. Still some tweaking and optimization is required. While cleaning is the most important change required in wet-chemical station of HJT processing, which was also extensively discussed in our previous article Cleaning Is Key, the remaining two processes – saw damage removal and texturing – also require some optimization.
In saw damage removal, about 6 µm of silicon is removed from each side of the wafer in the case of PERC, while it is 14-18 µm/wafer (total etch removal) for HJT, according to Thomas Künzl, product manager at Singulus Technologies, headquartered in Germany.
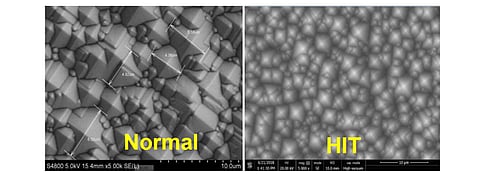
HJT also requires a more carefully optimized texturing process, as the size of the pyramids formed via this process influences reflectivity. High texture uniformity is an import change required for HJT. Then, optimization of the pyramid size can improve the reflectivity by about 1%. The goal here is to attain the best trade-off between optimum light trapping and high-level surface termination, which collectively helps in attaining low surface recombination velocity after PECVD passivation processes. Maintaining high surface uniformity is also very important in order to provide a better interface between the crystalline silicon textured surface and the deposited amorphous silicon layers. An important development associated with texturing tools has been to move away from an IPA based process to additives, which is also applicable to other cell technologies.
For detailed information on wetchemical process in HJT cell production, please download and read TaiyangNews report on Heterojunction Solar Technology 2020, which can be downloaded for free here.
A comprehensive overview on "Wet Chemical Boost for High Efficiency Passivated Contact Cells" was provided by RENA Head of Technology Holger Kuehnlein during the TaiyangNews High Efficiency Solar Conference – the recording can be viewed here.
