
Power is the most important characteristic of a module, next to efficiency, given it also serves as the primary sales metric for a PV panel. Furthermore, power indirectly determines the module's application since it generally relates to size. Although there is no hard and fast rule, solar modules are typically categorized into different applications based on their power rating. Usually, modules with a power rating of less than 500 W are preferred for residential applications, 500 to 600 W for commercial and industrial (C&I) applications, and above 600 W for utility installations. We have also followed the same analogy for power analysis.
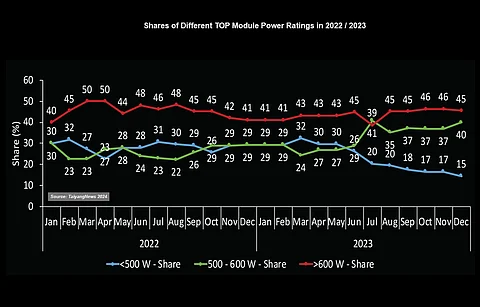
When we look at the product count of modules bifurcated into these 3 power classes, the TOP MODULES listing – which reflects the commercially available high-efficiency modules – is clearly dominated by high-power modules with a rating of greater than 600 W. The number of products increased steadily from 6 to 14 by the end of 2022 and then to 25 by the end of 2023.
However, its share overall has been the most consistent, varying mostly from 40% to 45%. The other classes have been fluctuating much more. The count of products with power ratings in the range of 500 W to 600 W increased from 5 to 10 by the end of 2022, and to 22 by the end of 2023. This power class was in the growth mode at least during H2-2023. Its relative share increased from 30% to 40% over the period of 2 years. The number of small modules increased from 6 to 10 by the end of 2022, while slightly decreasing to 8 by December 2023. This power class lost half its share in the total count of products from the beginning of 2022 to December 2023, from 30% to 15%. Together with the fact that the residential segment is booming, the indications are clear that more and more module makers are promoting modules above 500 W also for this application.
The text is an excerpt from the TaiyangNews TOP MODULES Analysis 2022 / 2023 Report, which can be downloaded for free here.
