- The TaiyangNews Solar Power Plant Developments 2024 Conference delved deep into the utility-scale PV project application
- Conference participants discussed the various new developments in the space while reflecting on how they are navigating through the challenges
- Co-location of solar with other technologies, permitting and policy changes are some of the topics the executive panelists touched upon
The global solar PV market continues to expand with growing demand, and while the industry faces various challenges—not limited to supply chain, grid connections and financing costs—it continues to press ahead with technological advancements.
The TaiyangNews Solar Power Plant Developments 2024 Conference brought together representatives from leading global players in the module, inverters and solar tracking space on the product supply side and buyers to discuss the latest advancements in utility-scale PV power plants. The participants also touched upon the various challenges for developers, EPC and O&M providers.
The Head of Strategy at Bulgarian utility-scale solar construction company Sunotec Group, Alexander Zahariev started the conference, presenting an overview of the status, challenges and solutions in PV power plant development, EPC and asset management.
The Europe-focused solar company, which is active from development to O&M and battery storage maintenance, has already established 8 GW capacity across Europe with its key markets being Denmark, France, Germany, UK, Poland and the Netherlands. As of March 2024, Sunotec had a pipeline of 12 GW; it said it installed 2.3 GW in 2023 and had a market share of 12% in the EU and UK.
Sunotec Group’s Alexander Zahariev presented an overview of the status, challenges and solutions in PV power plant development, EPC and asset management space. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
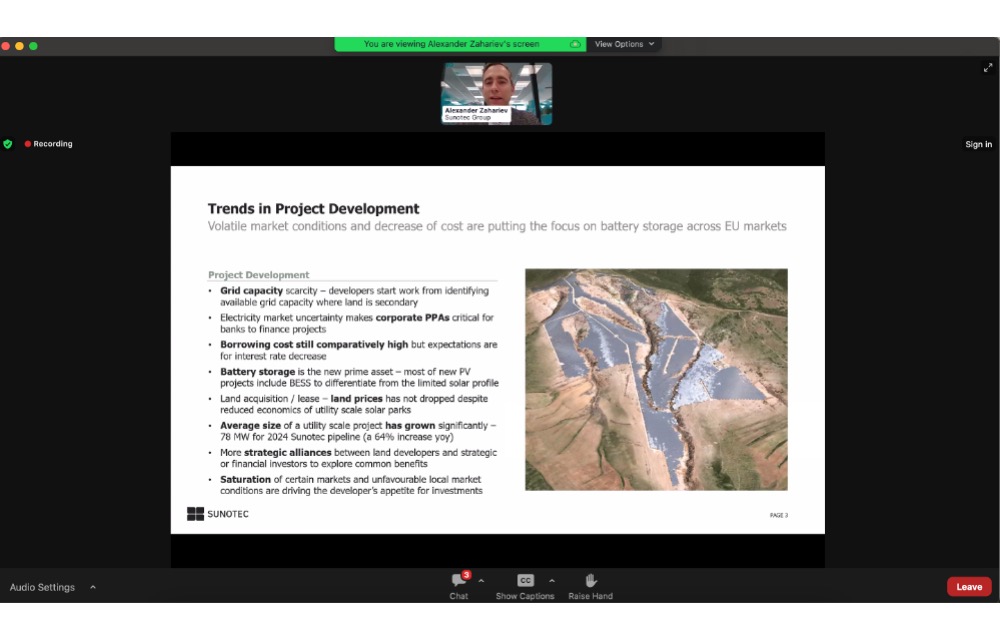
A crucial trend for solar development that Zahariev shared relates to investment in battery energy storage system (BESS). Calling battery storage the ‘new prime asset,’ he said most new PV projects include this to differentiate themselves from the limited solar profile. BESS also works well in case of hybrid or co-located facilities.
Corporate PPAs continue to be popular as these are critical to finance projects in times of electricity market uncertainty and even banks insist on them. Speaking of finance, borrowing costs are still high as the industry hopes for interest rates to come down.
Zahariev shared a new trend in Europe with big developers asking for strategic alliances with the contractors to secure the pipeline, meaning there are significant capacity bottlenecks for installations in Europe. The big boys in Europe are trying to put themselves in an exclusive position or to secure fixed capacity for them that can be delivered in the next year. This is very unusual for the solar market and a trend that’s not been seen until a few years ago.
The current level of investments in the market is driving solar power development in one direction. Sooner or later, Zahariev forecasts saturation in some European markets or Europe as a whole. Investors are trying to change their investment priorities from one market to the other.
For instance, Spain used to be a big investment destination, but now we can expect investments flowing into some Scandinavian nations such as Sweden and Finland where land is available and cheaper. These nations provide necessary returns and consumption for the projects to be viable.
In terms of EPC, there is a significant change coming into the market. While earlier the roles and responsibilities of developers and EPCs were clearly demarcated, this traditional setup has changed over the last few years since most big developers now prefer to save money by procuring and do most of the engineering on their own. The EPC scope of service is now very limited to only parts of the original setup. EPC now has to change to fit the developers’ requirements.
At the same time, EPC companies have now become picky in terms of choosing their clients. They look for clients they have a certain relationship with, to ensure payments are on time and supply chain is organized, especially for solar panels, transformers and inverters. In this manner, the installation schedule is met on time as standing time is the biggest enemy of an EPC company.
Here, Zahariev said pricing is not as important as timeline and quality. Time is critical to investors now.
Even on the O&M side, it is a changing game. Compared to 3 to 5 years ago when it used to be perceived as a zero-maintenance business, O&M’s role has now become important, thanks to the changes brought in by artificial intelligence (AI). It is now becoming more sophisticated with a larger scope of work including advisory services for clients, waterless module cleaning, and data collection to run precise models that will become important for energy trading in the near future. O&M today is more complex and data driven, which helps a developer figure out how to prevent disasters. It lends them a competitive edge.
The future opportunities for the downstream solar industry lie in repowering and secondary markets. It also makes sense when the primary development market in Europe starts to saturate, European companies should be ready to share knowledge, capacity and technology with Africa as it is the next big opportunity for solar.
JA Solar’s Xueshan Yang argued in favor of rectangular wafers bringing in uniformity and streamlining the supply chain in the industry. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
Chinese solar cell and module manufacturer JA Solar’s Product Manager Xueshan Yang shared the trends in advanced PV module design and customer value analysis.
Calling 2023 as the year of n-type, Yang said it will be the most important and most wanted module in the market over the next few years. With n-type, the module output is also increasing to up to 700 W. Any company with no n-type product in its portfolio has probably no competitive edge in the industry, at least in 2024, she claimed. Another important trend she highlighted is that modules are increasingly becoming application-sensitive. More and more customers are asking for special BOM in order to be more suitable for designated applications.
JA has picked the small-spacing path for high-density encapsulation, as against the other available techniques of conventional spacing, shingling and tiling ribbon. This small-spacing technique has now become the mainstream for high-density encapsulation thanks to its contribution to power improvement, product yield and reliability.
Yang shared case studies of PV projects in various applications to bring a customer value analysis and show the benefits of its DeepBlue modules.
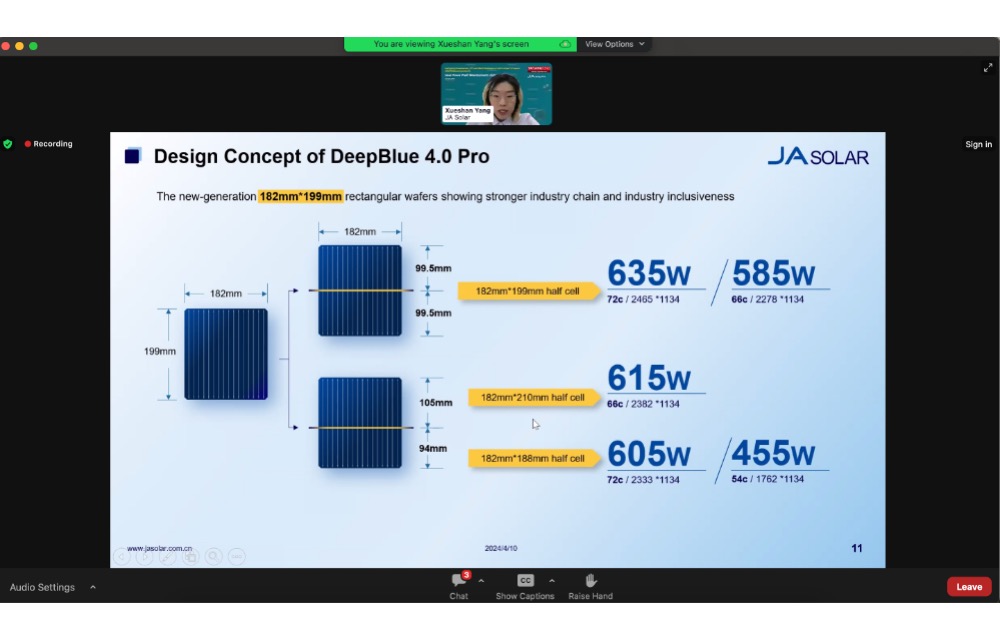
JA Solar uses n-type technology for its flagship product DeepBlue for which it uses a rectangular wafer size of 182 mm x 199 mm. One highlight of DeepBlue 4 Pro is its lower Voc compared to 78 cells in the same module dimension. At the module end, it reduces the risk of hotspots, and on the system end it allows more modules to be installed in one string, thereby reducing costs. Yang added, “That’s how JA brings value to our valuable customers.”
The DeepBlue 4.0 Pro has a dimension of 2,465 mm x 1,134 mm. Cutting the rectangular wafer in both asymmetrical and symmetrical manner provides various module sizes based on different (half-cut) wafer sizes.
Batting for rectangular wafers, Yang explained that these not only effectively increase the module power, but also make it possible to produce 4 major standard module products using only one wafer size. This is then applicable for various applications. Thanks to this flexibility, JA also produces customized modules for its customers.
Compared with equivalent products in the industry, Yang said it has significant manufacturing cost advantages and greater customer value.
TrinaTracker’s Sun Kai listed the benefits of digitalization in solar power plant maintenance, including a 3D digital map, using its smart controlling systems for trackers. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
The Head of Smart Tracker Control System at China’s TrinaTracker, Sun Kai talked about how digitalization boosts energy efficiency in PV power plants.
Calling digital technologies as the ‘golden keys’ to the future of PV towards a net zero world, Kai pointed to their growing use in the industry already in terms of design, construction, commissioning, and operation and maintenance.
In terms of tracking solutions for large-scale projects, Kai listed the shortcomings of a traditional tracking system that cannot effectively deal with challenges of shading loss, sensor failure and low battery, among others.
Presenting Trina’s Smart Tracking Solutions such as Vanguard 1P and 2P, Agile 1P, Kai said these provide high reliability, high performance and high efficiency. Smart monitoring and control, smart O&M of its solutions can be used to collect, share and analyze data.
It also introduces a 3D digital map functionality, providing intuitive and vivid representation of tracker layout and operational status. It is aimed at enhancing the ability of the maintenance personnel to carry out their work effectively, he explained. They can identify and manage risk while minimizing failure with the help of this 3D tool.
Kai said Trina’s patented technology of smart tracking algorithm (STA) and smart backtracking algorithm (SBA) makes its SuperTrack a highly reliable tool to improve power generation and reduce generation losses by integrating diverse data such as meteorology, topography, etc.
Huasun Energy’s Christian Comes revealed the company’s plans to venture into commercial production of HJT-perovskite tandem modules, latest by 2027. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
Chinese heterojunction (HJT) solar cell and module producer Huasun Energy’s Director of Business Development Europe, Christian Comes discussed the state-of-the-art high efficiency HJT technology in 2024.
Comes categorically stated that HJT is not a new technology and that it was already commercially established in 2005 after Japan’s Sanyo introduced it in 1997. Hence, that gives an advantage to HJT vis-à-vis TOPCon, which is comparatively a newer cell technology.
Both its installation cost and performance are better than TOPCon, claimed Comes, adding that HJT today brings more LCOE. By 2025, he expects HJT will benefit from low costs, thus matching the cost of TOPCon. At that point, it will not just become mainstream, but a leading technology and not just made by Huasun, but by many more.
When compared with TOPCon’s 22%, HJT has a higher efficiency of 23% in mass production. The latter also has a higher bifaciality of 85% as against 80% for TOPCon and a better temperature coefficient of 0.24%/C, while that of TOPCon is 0.29%/C.
Comes stressed that HJT with 2-side contact performs even better on all these parameters when compared to TOPCon with back contact cells.
For utility-scale, bifaciality works better; and as vertical modules are proposed in the future, HJT with its higher bifaciality works better.
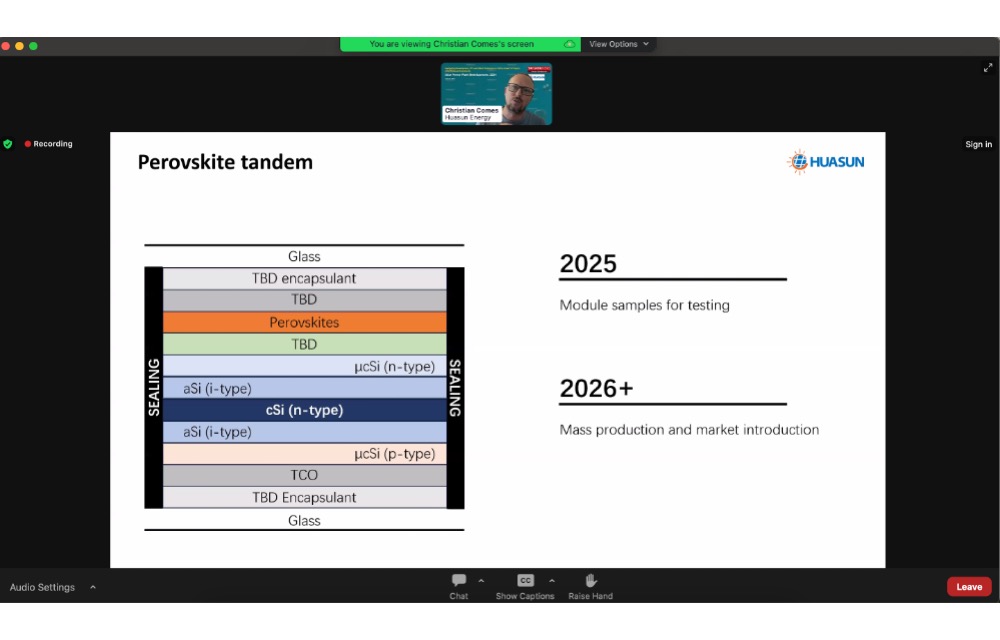
Calling HJT the best platform for perovskite, Comes said Huasun plans to launch perovskite-HJT tandem module samples for testing in 2025, aiming for mass production and market introduction in 2026 or 2027 with 28% or 29% module efficiency.
Aquila Capital’s Ozer Ergul stressed on the importance of transparency and traceability for the solar energy industry. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
German investment company Aquila Capital’s CPO Ozer Ergul delved into the ESG considerations in procurement in his presentation, a hot topic these days.
Reflecting on the current market challenges, Ergul pointed to supply chain security as a problem area. Supply risks emanate from the significant increase in demand for renewables for energy security, while supply of key materials remains limited and concentrated.
Inflation is another pain point that makes supply chain disruptions across industries and geographies more intense. Businesses, he pointed out, can no longer give a sure or fixed price for projects, equipment and supplies due to these reasons.
Technology maturity and rate of market adoption for innovation is challenged by material availability, cost and reliability challenges.
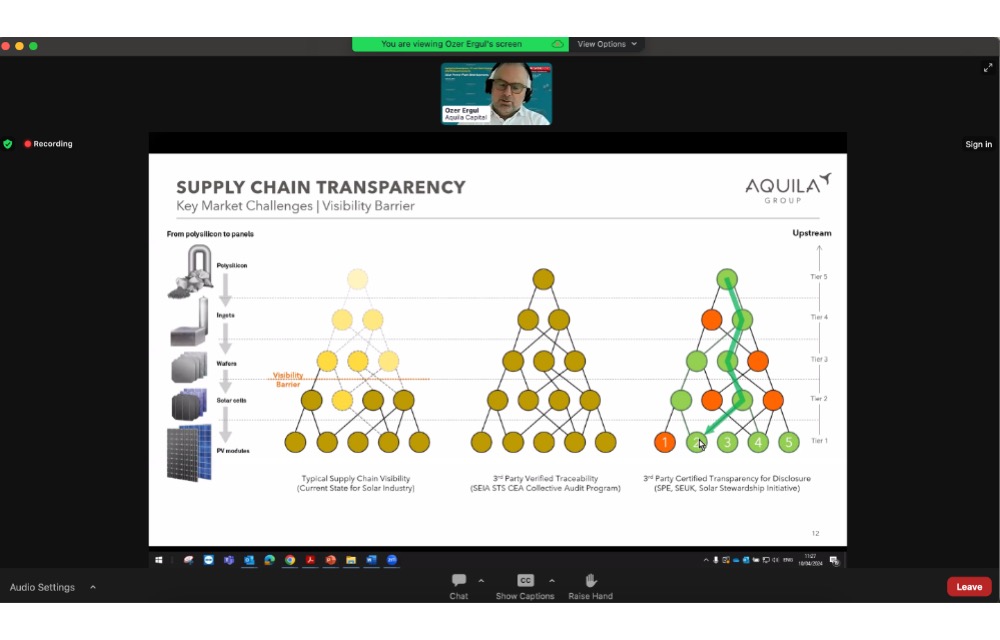
In between all this, traceability and transparency of supply chains is becoming an important aspect across the world as countries prioritize the impact of both downstream as well as upstream processes in the production of clean technologies like solar PV.
In the wake of forced labor issues in the solar supply chain, there is a growing clamor for supply chain transparency. Referring to Europe’s Solar Stewardship Initiative, Ergul stressed on the industry’s attitude to switch from compliance to commitment as transparency, sustainability and social impact governance become crucial for the industry.
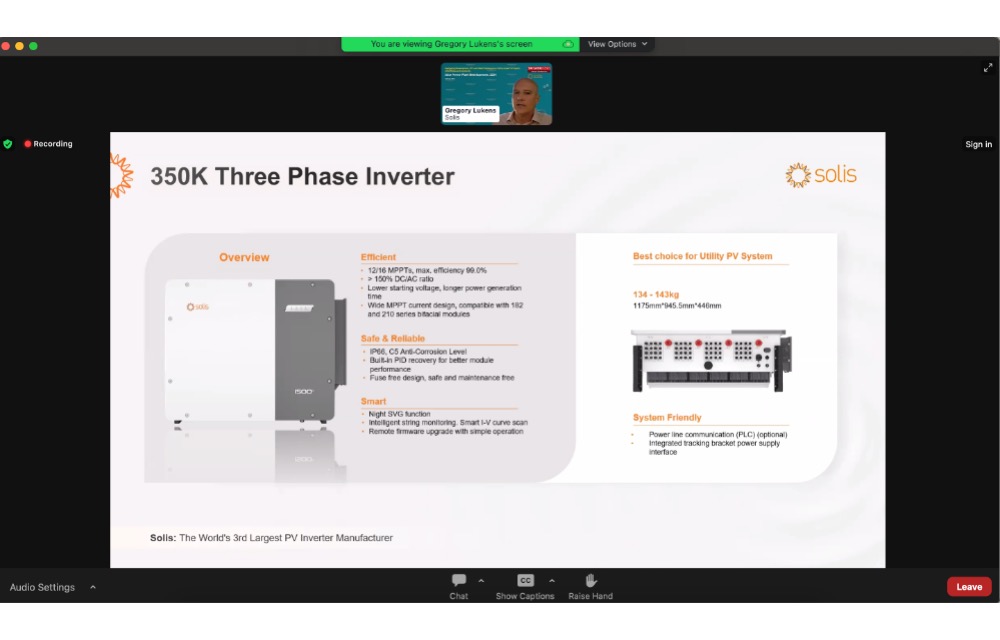
Solis’ Gregory Lukens said the manufacturer is set to launch a new 350 kW string inverter product in Europe for utility-scale applications. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
The Utility Director Europe for Chinese string solar inverter company Solis, Gregory Lukens, discussed string inverters for utility-scale projects at the conference. Part of China’s Ginlong Technologies, Solis has an annual string inverter production capacity of 80 GW. It aims to increase it to 120 GW by 2025.
Lukens said Solis has based the business on the solid foundation of supply chain. For its IGBT needs, which is the beating heart of an inverter, it uses one from Germany’s Infineon for all its inverters being sold outside of China.
It already offers a 250 kW inverter in Europe. The company is set to launch its 350 kW 3-phase inverter to be available for delivery in Europe in Q1/2025. Currently, it is being tested in China. Solis also caters to the solar industry with a transformer station. It is primarily manufactured in China, but the manufacturer said it is also working with local European component manufacturers.
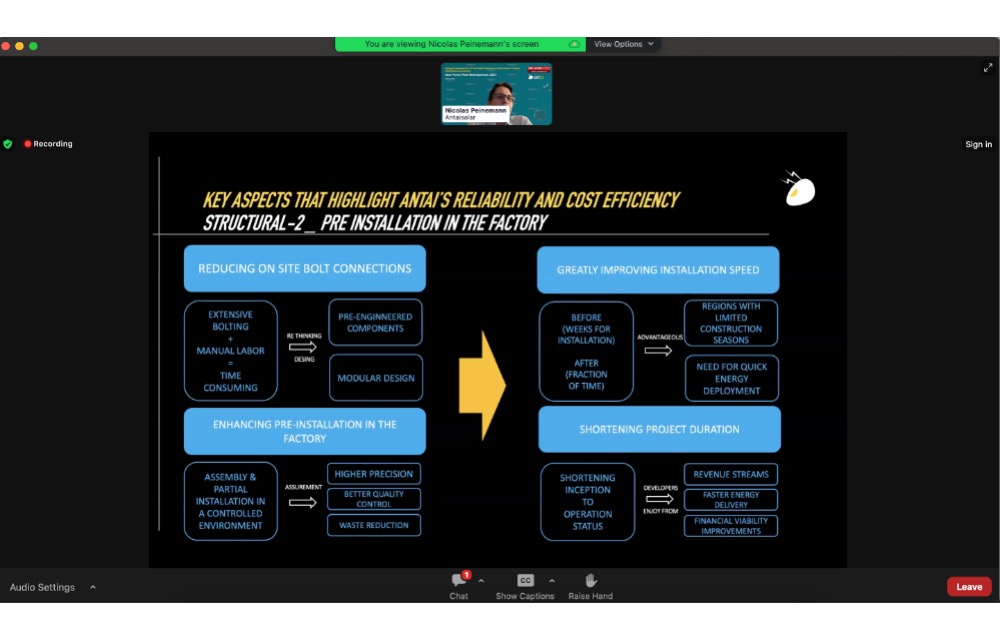
Antaisolar’s Nicolas Peinemann listed the ways structural system suppliers can support utility-scale solar project developments with innovation and technology. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
Chinese solar tracker solutions company Antaisolar’s Sales Director for Latam and Iberia region, Nicolas Peinemann shared the company’s tracking system solution, claiming that it enhances reliability and cost efficiency.
Going by the challenges a utility-scale solar PV project faces right from development to O&M and financial constraints, Peinemann discussed the role of a structural system supplier like Antaisolar to enhance reliability and cost efficiency of such a project.
Among the key strategies he categorized to positively impact utility-scale projects, Peinemann stressed certain key moves, starting with structural suppliers to focus on using advanced materials and design. This entails using the right materials and geometries.
Pre-installation in factories will help ensure faster installation, higher precision, waste reduction and reduced time for installation on the actual site. Improving control algorithms will ensure tailored products to optimize system performance.
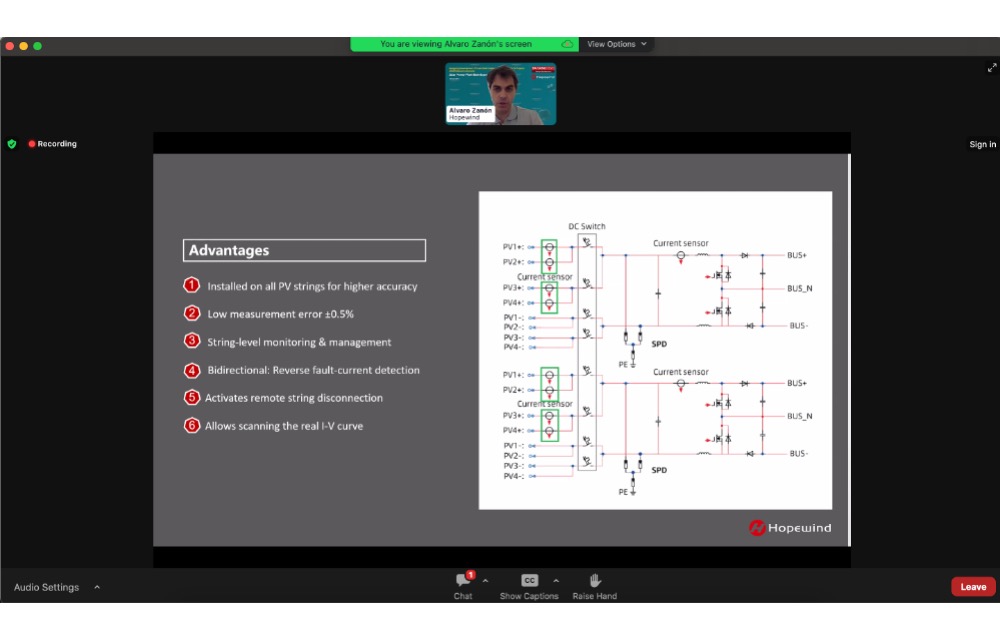
Hopewind’s Alvaro Zanon shared the various features of the company’s string inverters, including intelligent string monitoring. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
Another Chinese solar inverter manufacturer Hopewind’s Global Technical Director—Utility Projects, Alvaro Zanon pointed to the important role of digitalization in the safety and O&M of utility string inverters in his presentation.
Having originated in the wind energy space as wind converter supplier, Hopewind has diversified into the solar sector providing string and central inverters and its energy management system, among others. It is currently in the process of expanding outside of China with its central inverters up to 3.5 MW.
Talking about the company’s utility-scale string inverters, Zanon said its 385 kW inverter is the largest string inverter in the market. It also provides transformer stations.
Zanon listed the various features of Hopewind’s string inverters including intelligent string monitoring, which it has installed on all PV strings for higher accuracy. This enables low measurement error, and allows for string-level monitoring along with scanning the real I-V curve.
Among other features, its inverters incorporate an intelligent DC switch with 4 strings/MPPT, and DC & AC terminals’ temperature detection. The latter is a new feature from Hopewind that aims to help with temperature assessment of the specific terminal. If the threshold is exceeded, it will trigger the protection terminals.
Arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) is helpful when it comes to poor contacts, damaged wires, aging, corrosions, or loose PV wire connections. It can protect against fire and short-circuits with 100% detection accuracy.
Zanon said AFCI is now covered by the IEC standard 63027 released in May 2023. It is now up to individual countries to make it mandatory for their PV installations. Hopewind includes this feature in all its inverters by default.
Hopewind’s inverters also include 8 built-in smart air-cooling fans. This feature ensures lower operating temperature and extends component lifetime with lower operating costs. These can be replaced in an existing installed inverter.
Zanon added performance induced degradation (PID) to its list of features along with I-V curve diagnosis. The latter helps prevent energy losses and checks 100% PV strings in a few minutes. It can be performed via hopeCloud software.
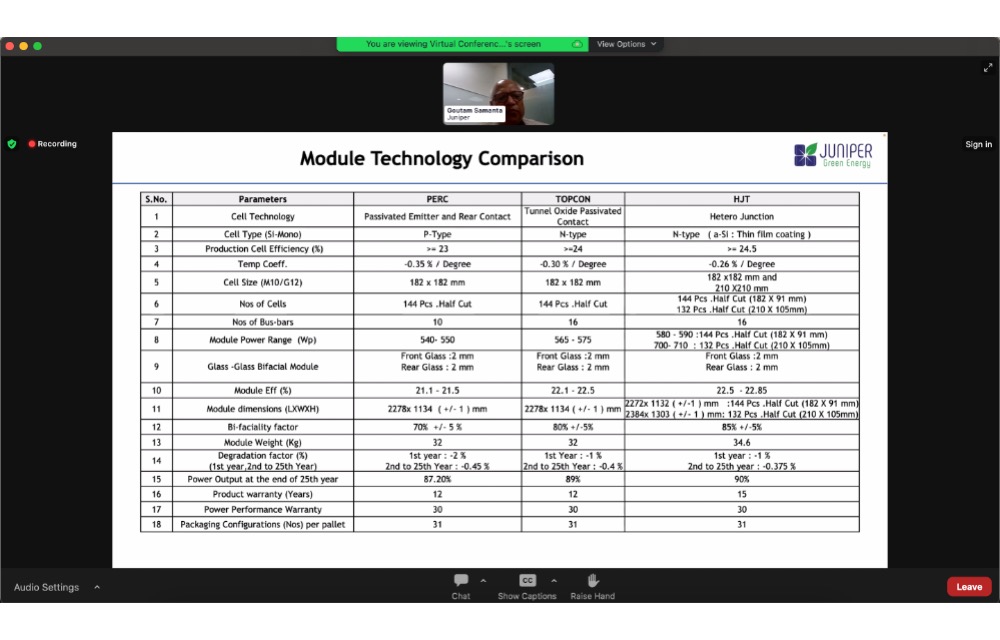
Juniper Green Energy’s Gautam Samanta compared various module technologies for successful operation in the Indian context and recommended high wattage modules with low temperature coefficient as perfect. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
Head of PV Technology at Indian renewable energy independent power producer Juniper Green Energy, Gautam Samanta shared the procurement and system design strategies in the low-cost solar market of India.
Encompassing the various aspects of engineering, procurement and construction, Samanta said the selection of solar modules is of paramount importance for system engineering.
Providing a module technology comparison chart, Samanta recommended using 540 W or higher wattage modules for the Indian context with a bifacial double-glass configuration and anti-soiling features. String inverters work best along with single-axis trackers, among other features. The high-temperature and humid Indian climate demands a product with a low temperature co-efficient.
Calling procurement a bridge between engineering and construction, Samanta recommended various strategies to select the right components, including global sourcing to take competitive advantage from low-cost countries.
When it comes to large-scale projects, Samanta recommended taking the plot approach to building such facilities. Under this, dividing the project in various small sub-plots is a good design yield approach that leads to optimum utilization of resources and efficient supply chain control, he added.
Talking about trackers, the conference had US-based solar tracker manufacturer Nextracker’s Senior International Director EU Antonio Sendin and Senior Business Development Manager EMEA Antonio Buiza discussing the company’s performance software, calling it solar power’s secret weapon for Europe’s northern latitudes.
The duo talked about Nextracker’s TrueCapture technology, which they define as an intelligent, self-adjusting tracker control software. Using diffuse and row-to-row (R2R) modes, they claim it increases typical PV power plant energy by up to 4% annually. The split boost mode under R2R brings an additional level of optimization, they added.
Speaking with TaiyangNews’ Michael Schmela, Nextracker’s Antonio Sendin and Antonio Buiza, and GRIDSERVE’s Michael Vassakis said they believe the tipping point for trackers to become a standard for utility-scale PV has been reached. (Photo Credit: TaiyangNews)
TrueCapture is part of Nextracker’s advanced software license model that also includes Navigator HMI. The latter covers Hail Pro that covers hail stowing, flood stowing, snow stowing, etc. This software can bring the trackers to a hail stow position before hail actually begins. These bankability features ensure financial gains.
The CTO of solar powered electric vehicle charging solutions company GRIDSERVE, Michael Vassakis also shared the company’s experience of having deployed Nextracker trackers with TrueCapture in its projects.
GRIDSERVE is a hybrid solar farm specialist from the UK. Sharing the example of the company’s York Hybrid Solar Farm, which was the 1st subsidy-free solar project in the UK, Vassakis said it was commissioned in 2019. It uses Nextracker trackers. Post the commissioning, GRIDSERVE selected 2 blocks out of it to measure the benefits of TrueCapture.
The 2 blocks using Nextracker’s software suite reported gains of 0.95%, and the other 0.82%. This was against the originally estimated gain of 0.74%. This proved the efficacy of the tracker configuration provided by Nextracker.
Vassakis said he believes that as the industry moves forward with higher degree of innovation, module prices are likely to go up in the future. These will then need trackers with a technology like TrueCapture to dependably support projects.
Both Sendin and Buiza pointed to the York farm to show the financial and energy benefits of installing trackers in the northern latitudes. Trackers with software controlling functions are even better at optimizing a system. They shared that the company is now working in various European markets including Latvia.
Trackers also help generate electricity through the day ensuring stable output, and when combined with storage, a solar project can benefit the most.
Vassakis added that the tipping point for trackers to become a standard for utility-scale installations has already been reached.
Executive Panel
Moderated by TaiyangNews Managing Director Michael Schmela, the executive panel explored the development, EPC and O&M challenges in utility PV projects amid financial constraints.
For Juniper Green Energy’s Gautam Samanta, land acquisition is the biggest challenge for solar developers in the Indian context. Most projects currently work on the leasing model. Additionally, he discussed the impact of reinstating of the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) as limiting module procurement options.
While there is some 60 GW module capacity available in India, the country still relies on China for cells. DCR compliance modules are expensive and won’t be enough for the 30 GW odd annual installations the country needs to achieve by 2030 to meet the 280 GW solar PV installation target.
He called for revisiting the ALMM to be implemented in phases so as to allow Indian manufacturing capacity to pick up pace. Samanta believes the Indian government considers including some Chinese companies in the ALMM to enable this scale of installation target to be achieved.
GRIDSERVE’s Michael Vassakis pointed to the lack of grid capacity as the biggest hurdle for solar PV’s smooth growth in Europe. In its absence, developers suffer financially.
He also believes that while solar PV is big enough, it can’t work in isolation as the world targets a low-carbon energy transition. It needs to be complemented with storage, wind, etc., in a hybrid mode to ensure system flexibility.
Aquila Capital’s Ozer Ergul listed permitting as the biggest challenge for solar project development as without this a project cannot even start. Permitting is handled by bureaucracy that doesn’t have a sense of urgency.
Additionally, in the European context, there is no contiguous stretches of land available for larger projects. This demands innovation and collaboration for the markets. He agreed with Vassakis’ suggestion of co-location of solar projects in hybrid mode to achieve the targets.
Ergul also stressed on bringing transparency to the industry with suppliers coming clean with the right products. Compared to this, pricing isn’t as big a challenge for Europe at present.
TaiyangNews will be back with its next conference on May 7 and 8, 2024 on Cell & Module Production Equipment & Processing Materials. Registrations are already open here.