- DOE’s issue brief on solar energy expects it to play an important role helping the US achieve its carbon pollution free goal for its power sector by 2035
- It lists the opportunities scaling up solar energy can bring to the US in terms of ‘good quality’ and bringing down electricity costs
- US President Joe Biden led administration believes its Build Back Better agenda and Bipartisan Infrastructure Deal investments will help explore the potential of solar in the country
Large scale decarbonization of electricity sector could mean solar power to account for more than 40% of the US electricity mix, from 3% at present, according to preliminary results of an upcoming National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) analysis that the US Department of Energy (DOE) refers to in a recent issue brief released.
As the White House aims for the US power sector to become 100% carbon pollution free by 2035, the current administration sees solar playing an important role in reaching President Joe Biden’s goal for clean electricity, alongside other sources as onshore and offshore wind, green hydrogen, geothermal and nuclear power, among others.
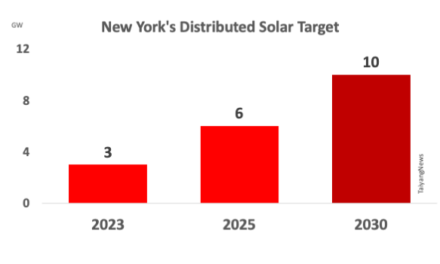
Titled Investing in a Clean Energy Future: Solar Energy Research, Deployment, and Workforce Priorities, the brief explores the opportunities solar energy industry offers to Americans, especially since its capacity is set to grow from more than 100 GW DC (see US Installed 5 GW DC New Solar Capacity In Q1/2021).
The analysis points out that, ‘solar is already the fastest-growing source of new electricity generation in the nation – growing from about 2.5 GW DC of solar capacity in 2010 to over 100 GW DC today.’ And despite the pandemic nearly 20 GW were installed last year, more than ever before – with a huge pipeline in different stages.
Currently, the US has 15 GW AC of utility scale PV projects under construction, 7 GW AC with regulatory approvals and 20 GW AC planned, reads the brief while referring to the Energy Information Administration (EIA) numbers. It also adds that at the end of 2020, more than 450 GW of solar and solar+storage projects had applied for interconnection to the bulk power system.
According to the NREL analysis, ‘solar deployment would need to accelerate to 3 to 4 times faster than its current rate by 2030’ in order to turn the power sector carbon neutral.
The current administration believes realizing this potential will require ‘historic’ investments across all segments including residential, commercial and utility scale solar systems. Efforts are on to bring down the cost of solar energy from current levels to $0.02 per kWh for utility scale, and to $0.05 per kWh for residential segment, without subsidies by 2030, which the administration believes will happen with further innovation (see US Aims To Cut Solar Energy Costs By 60% By 2030).
According to the White House, the Build Back Better and Bipartisan Infrastructure Deal investments proposed by President Biden could help DOE achieve these solar cost reductions, complemented by investments in clean energy R&D, supply chains of critical materials, and tax cuts for new and retooled factories for advanced energy manufacturing.
The DOE’s issue brief estimates close to 500,000 to 1,500,000 people working in the solar sector in the US by 2035 in ‘good-quality jobs with strong labor standards, including prevailing wages and the free and fair choice to join a union and bargain collectively’.
“The issue brief clearly demonstrates the massive growth in solar over the last decade and charts a course for solar to grow market share and reduce emissions of greenhouse gases,” said Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) President and CEO Abigail Ross Hopper.
The issue brief is accessible on DOE’s website.